Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Add nodal labels on plots#
You can add use label properties to add custom labels to specific nodes. If the label for a node is not defined or None, the nodal scalar value of the currently active field at that node is shown. If no field is active, the node ID is shown.
Import the dpf_core module, included examples files, and the DpfPlotter
module.
from ansys.dpf import core as dpf
from ansys.dpf.core import examples
from ansys.dpf.core.plotter import DpfPlotter
Open an example and print the Model object. The
Model class helps to organize access
methods for the result by keeping track of the operators and data sources
used by the result file.
Printing the model displays this metadata:
Analysis type
Available results
Size of the mesh
Number of results
model = dpf.Model(examples.find_msup_transient())
print(model)
DPF Model
------------------------------
Transient analysis
Unit system: MKS: m, kg, N, s, V, A, degC
Physics Type: Mechanical
Available results:
- displacement: Nodal Displacement
- velocity: Nodal Velocity
- acceleration: Nodal Acceleration
- reaction_force: Nodal Force
- stress: ElementalNodal Stress
- elemental_volume: Elemental Volume
- stiffness_matrix_energy: Elemental Energy-stiffness matrix
- artificial_hourglass_energy: Elemental Hourglass Energy
- thermal_dissipation_energy: Elemental thermal dissipation energy
- kinetic_energy: Elemental Kinetic Energy
- co_energy: Elemental co-energy
- incremental_energy: Elemental incremental energy
- elastic_strain: ElementalNodal Strain
------------------------------
DPF Meshed Region:
393 nodes
40 elements
Unit: m
With solid (3D) elements
------------------------------
DPF Time/Freq Support:
Number of sets: 20
Cumulative Time (s) LoadStep Substep
1 0.010000 1 1
2 0.020000 1 2
3 0.030000 1 3
4 0.040000 1 4
5 0.050000 1 5
6 0.060000 1 6
7 0.070000 1 7
8 0.080000 1 8
9 0.090000 1 9
10 0.100000 1 10
11 0.110000 1 11
12 0.120000 1 12
13 0.130000 1 13
14 0.140000 1 14
15 0.150000 1 15
16 0.160000 1 16
17 0.170000 1 17
18 0.180000 1 18
19 0.190000 1 19
20 0.200000 1 20
Get the meshed region.
mesh_set = model.metadata.meshed_region
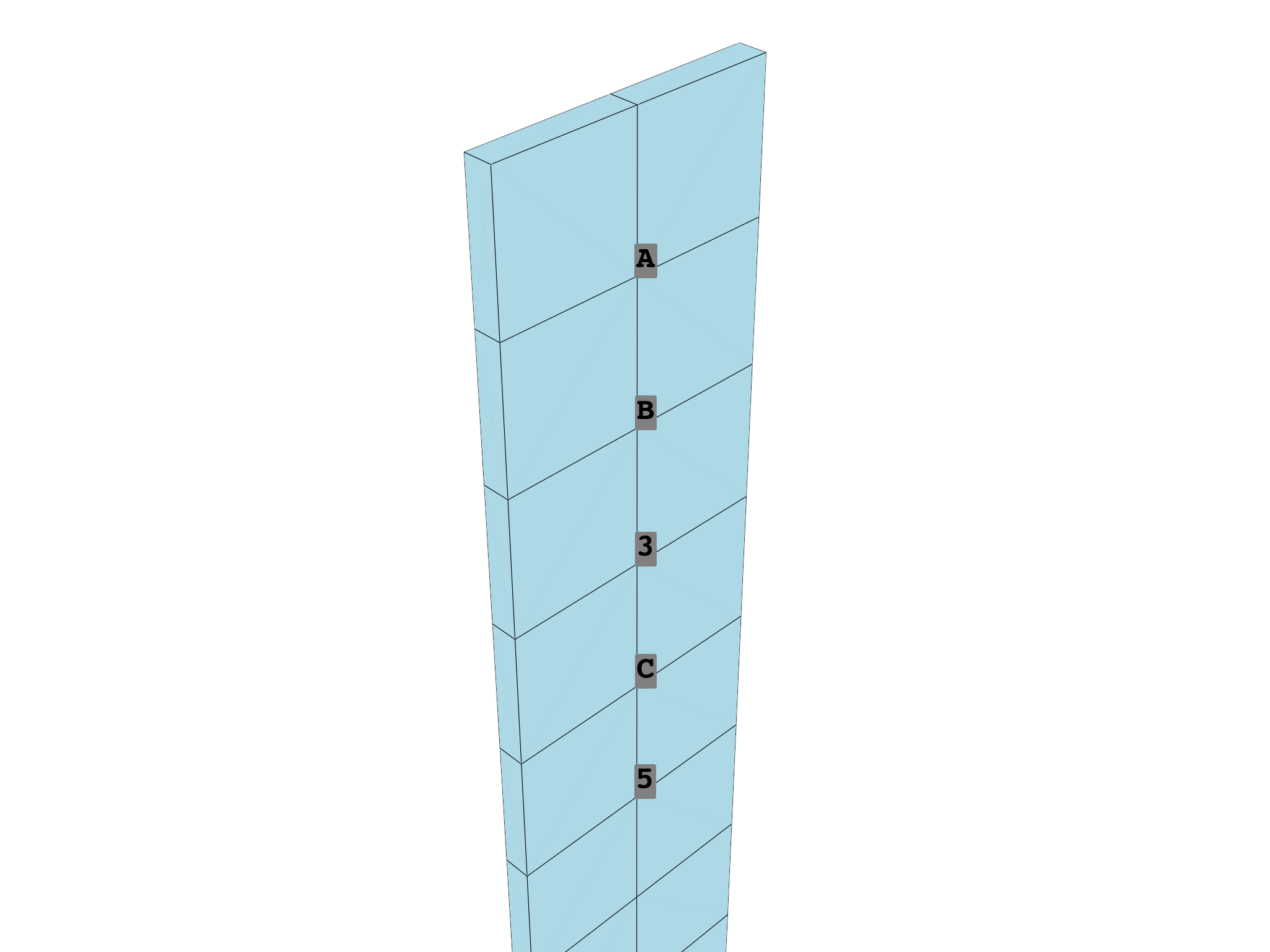
# One can plot the mesh with labels and/or node IDs shown
# for the first five nodes of the mesh.
plot = DpfPlotter()
plot.add_node_labels(
nodes=mesh_set.nodes.scoping.ids[:5],
meshed_region=mesh_set,
labels=["A", "B", None, "C"],
font_size=50,
)
plot.show_figure(
cpos=[
(0.3533494514377904, 0.312496303079723, 1.1859368974825752),
(-0.07891143256220956, -0.11976458092027707, 0.7536760134825755),
(0.0, 0.0, 1.0),
]
)
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 2
Get the stress tensor and connect time scoping.
Make sure that you define dpf.locations.nodal as the scoping location because
labels are supported only for nodal results.
stress_tensor = model.results.stress()
stress_tensor.inputs.time_scoping([20])
stress_tensor.inputs.requested_location(dpf.locations.nodal)
# field = stress_tensor.outputs.fields_container.get_data()[0]
norm_op = dpf.operators.math.norm_fc()
norm_op.inputs.connect(stress_tensor)
field_norm_stress = norm_op.outputs.fields_container()[0]
print(field_norm_stress)
norm_op2 = dpf.Operator("norm_fc")
disp = model.results.displacement()
disp.inputs.time_scoping.connect([20])
norm_op2.inputs.connect(disp.outputs)
field_norm_disp = norm_op2.outputs.fields_container()[0]
print(field_norm_disp)
DPF stress_0.2s Field
Location: Nodal
Unit: Pa
393 entities
Data:1 components and 393 elementary data
DPF displacement_0.2s Field
Location: Nodal
Unit: m
393 entities
Data:1 components and 393 elementary data
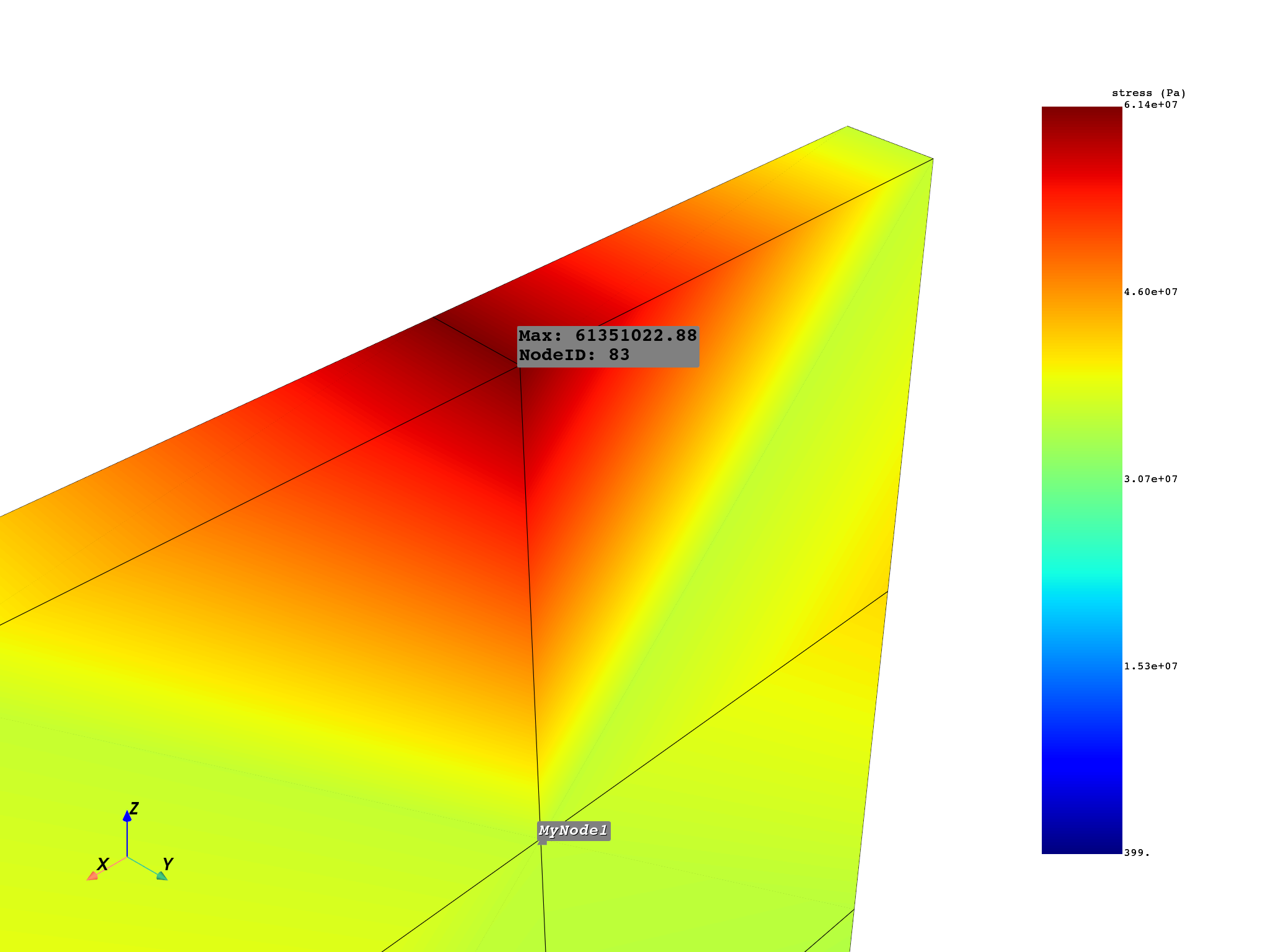
Plot the results on the mesh and show the minimum and maximum.
plot = DpfPlotter()
plot.add_field(
field_norm_stress,
meshed_region=mesh_set,
show_max=True,
show_min=True,
label_text_size=30,
label_point_size=5,
)
# Use label properties to add custom labels to specific nodes.
# If a label for a node is missing and a field is active,
# the nodal value for this field is shown.
my_nodes_1 = [mesh_set.nodes[0], mesh_set.nodes[10]]
my_labels_1 = ["MyNode1", "MyNode2"]
plot.add_node_labels(
my_nodes_1,
mesh_set,
my_labels_1,
italic=True,
bold=True,
font_size=26,
text_color="white",
font_family="courier",
shadow=True,
point_color="grey",
point_size=20,
)
my_nodes_2 = [mesh_set.nodes[18], mesh_set.nodes[30]]
my_labels_2 = [] # ["MyNode3"]
plot.add_node_labels(
my_nodes_2,
mesh_set,
my_labels_2,
font_size=15,
text_color="black",
font_family="arial",
shadow=False,
point_color="white",
point_size=15,
)
# Show figure.
# You can set the camera positions using the ``cpos`` argument.
# The three tuples in the list for the ``cpos`` argument represent the camera
# position, focal point, and view respectively.
plot.show_figure(
show_axes=True,
cpos=[(0.123, 0.095, 1.069), (-0.121, -0.149, 0.825), (0.0, 0.0, 1.0)]
)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.936 seconds)