Mesh and geometry#
通过 Mapdl 类,您可以访问网格和几何图形,而无需写入中间文件或解释各种 MAPDL 命令的文本输出。
例如,要访问模型的节点和达摩院,通常可以使用 Mapdl.nlist() 方法在 MAPDL 中列出节点。但是,这会生成一个字符串。
数组访问要么需要繁琐的 MAPDL GET 命令,要么需要将节点写入归档文件,然后用其他软件读入:
NLIST
LIST ALL SELECTED NODES. DSYS= 0
NODE X Y Z THXY THYZ THZX
1 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.00 0.00 0.00
2 1.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.00 0.00 0.00
3 0.2500 0.0000 0.0000 0.00 0.00 0.00
不过,通过 Mapdl.mesh 类,您可以与 Mapdl 类的当前实例接口,并使用此代码访问当前节点坐标:
>>> mapdl.mesh.nodes
[[0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[1.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.25, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.75, 0.5, 3.5],
[0.75, 0.5, 4.0],
[0.75, 0.5, 4.5]]
Mapdl.geometry 和 Mapdl.mesh 属性都支持对 MAPDL 数据进行额外的、较低级别的访问。您可以使用此代码访问它们:
>>> mapdl.mesh
>>> mapdl.geometry
要查看当前网格状态,可以使用此代码:
>>> mapdl.mesh
ANSYS Mesh
Number of Nodes: 7217
Number of Elements: 2080
Number of Element Types: 2
Number of Node Components: 0
Number of Element Components: 0
Geometry#
在 PyMAPDL 0.66.0 及以后版本中,默认情况下,所有几何实体都以 pyvista.MultiBlock 对象的形式返回。
Example 1
>>> mapdl.geometry.areas
MultiBlock (0x147ca7640)
N Blocks 28
X Bounds -0.016, 0.016
Y Bounds -0.008, 0.018
Z Bounds -0.003, 0.015
Example 2:
>>> mapdl.geometry.keypoints
MultiBlock (0x147a78220)
N Blocks 26
X Bounds -0.016, 0.016
Y Bounds -0.008, 0.018
Z Bounds -0.003, 0.015
如您所见,您不需要在新 API 中调用实体。
关于新版几何 API 与旧版几何 API 的更多区别,请参见 迁移到新的几何应用程序接口。
现在的“选择”方式也更容易了。
您可以使用索引:
>>> volume0 = mapdl.geometry.volumes[0]
>>> volume0
UnstructuredGrid (0x149107340)
N Cells: 34
N Points: 36
X Bounds: 0.000e+00, 1.588e-02
Y Bounds: -7.620e-03, 1.778e-02
Z Bounds: -3.180e-03, 0.000e+00
N Arrays: 3
您可以使用实体名称:
>>> volume1 = mapdl.geometry.volumes["volume 1"]
>>> volume1
UnstructuredGrid (0x149107340)
N Cells: 34
N Points: 36
X Bounds: 0.000e+00, 1.588e-02
Y Bounds: -7.620e-03, 1.778e-02
Z Bounds: -3.180e-03, 0.000e+00
N Arrays: 3
您可以通过调用 plot() 方法来绘制不同的实体:
>>> mapdl.geometry.areas.plot()
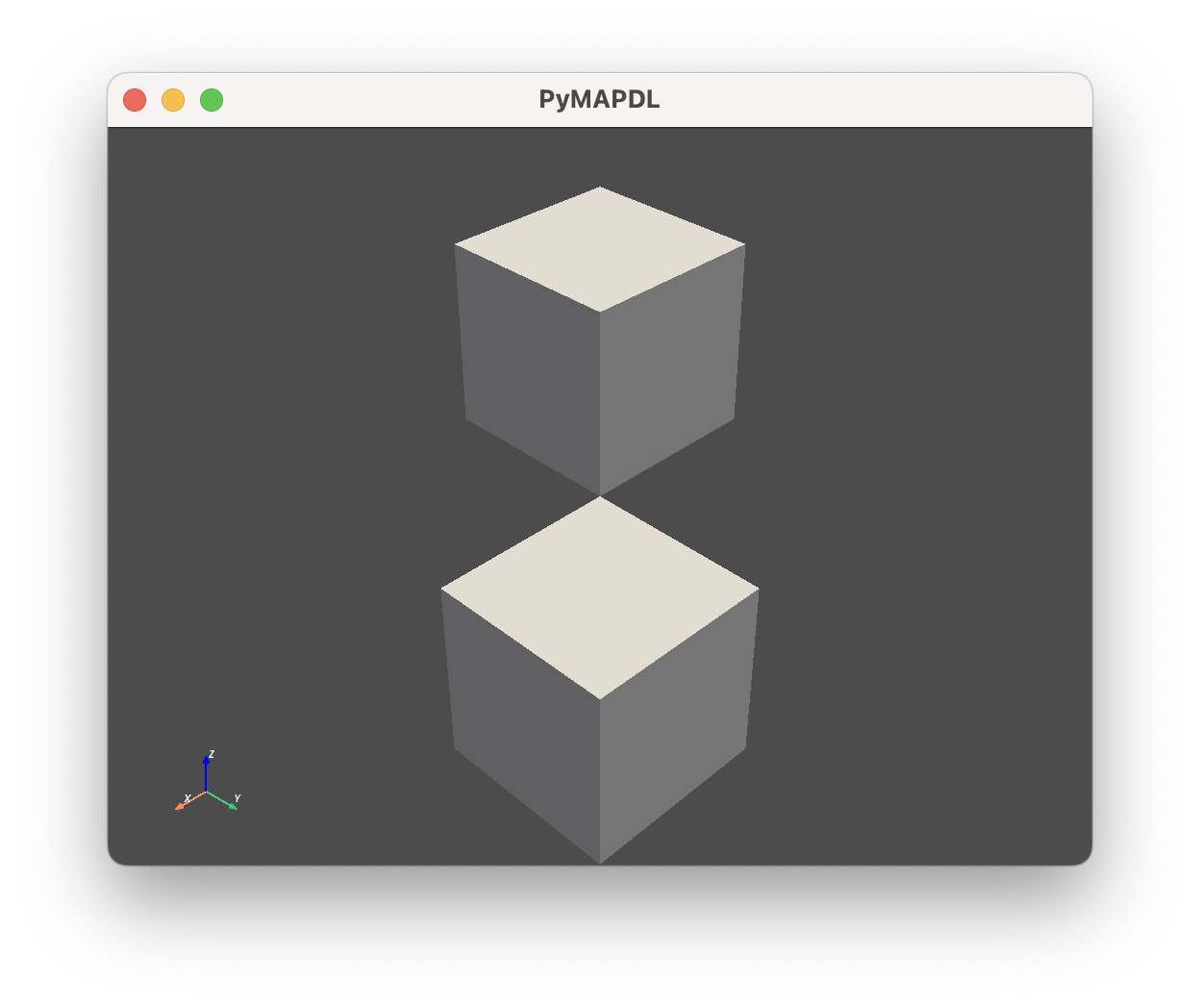
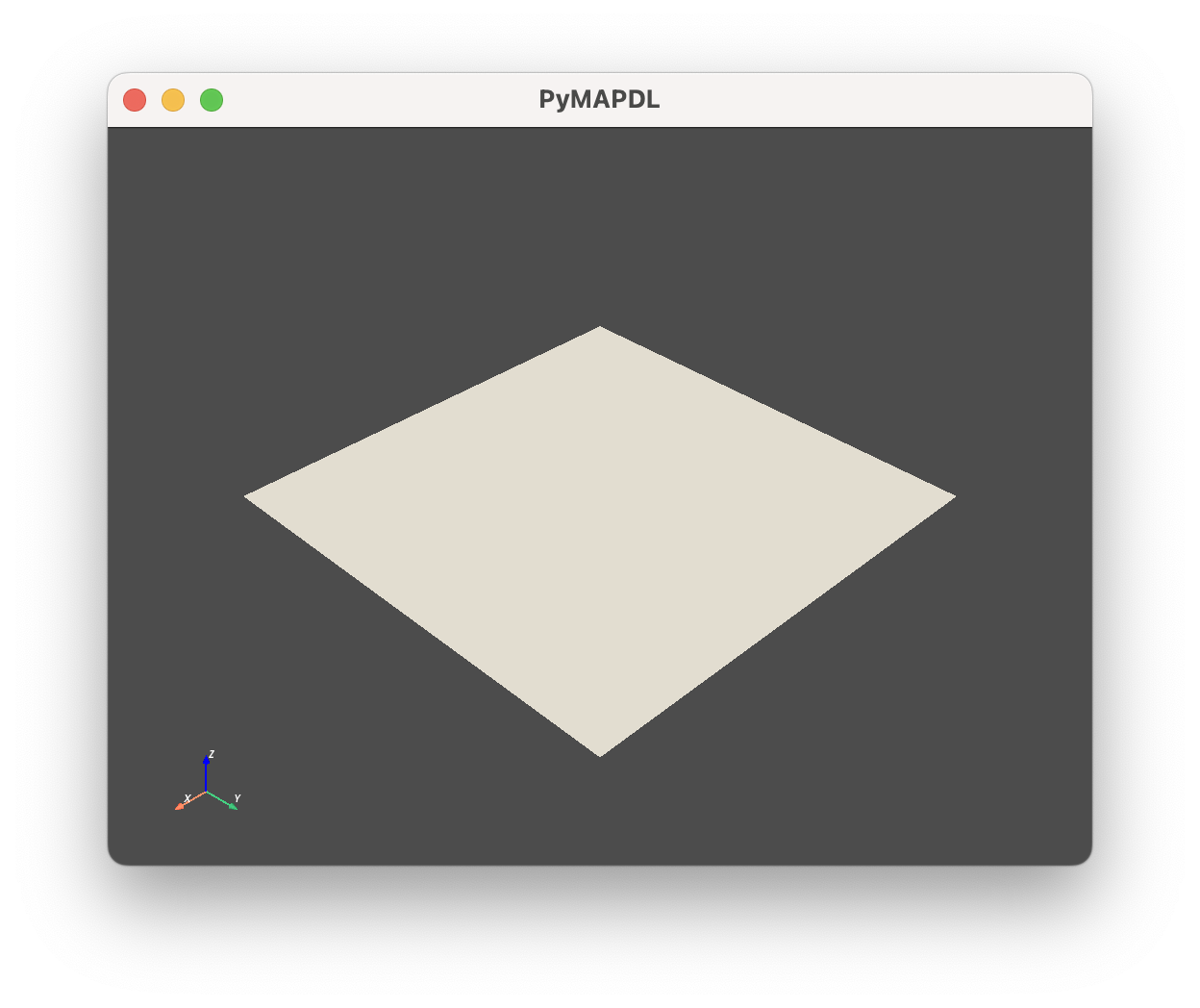
您可以绘制单个实体:
>>> mapdl.geometry.areas["area 1"].plot()
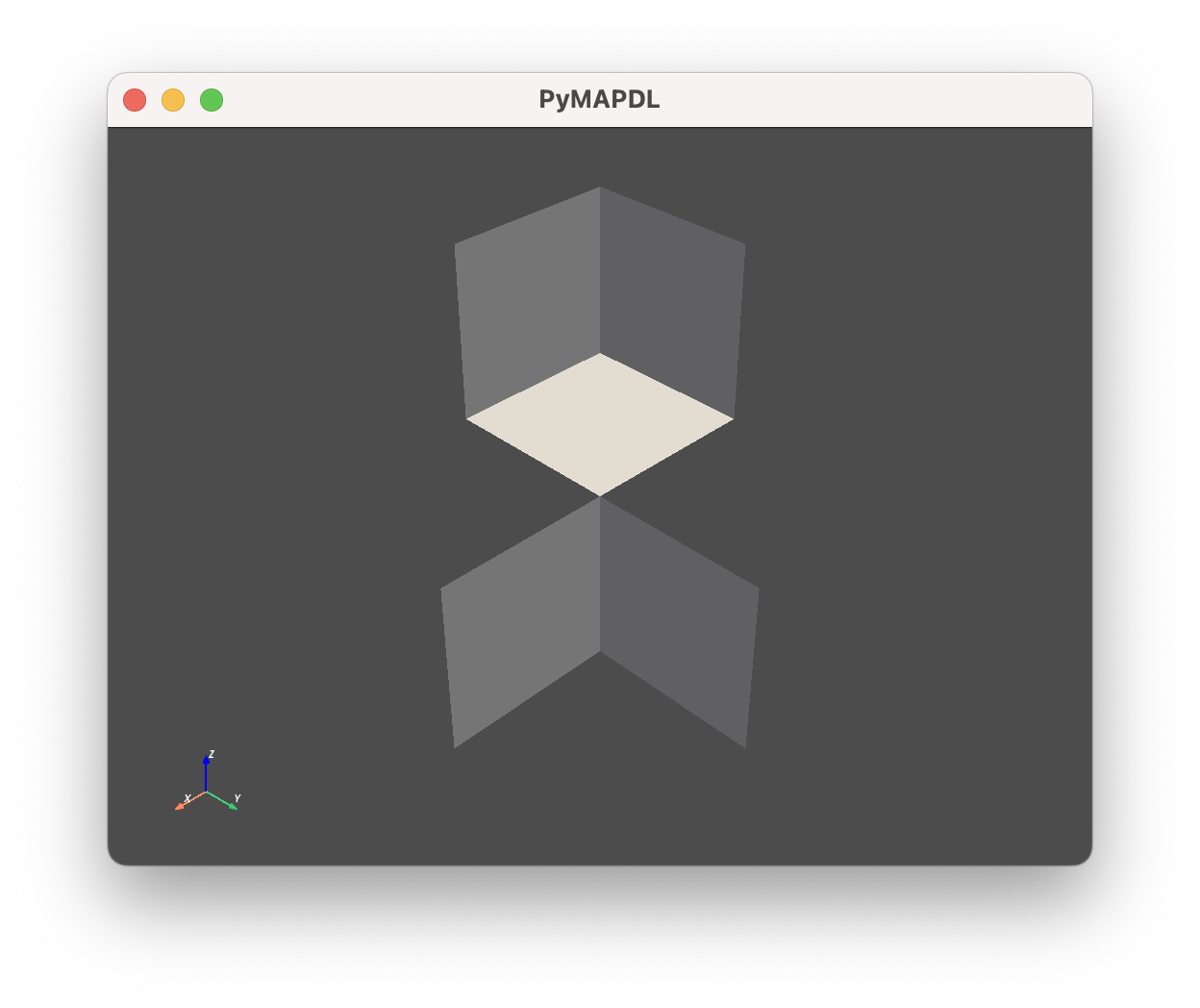
您可以使用切片绘制多个实体:
>>> mapdl.geometry.areas[2:12:2].plot()
此外,我们还提供了以下方法,将几何实体作为其他 Python 对象返回:
Table 1. Get_ENTITY methods.
Default output |
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
Not Applicable |
Not Applicable |
|||
Not Applicable |
Not Applicable |
|||
Not Applicable |
Not Applicable |
迁移到新的几何应用程序接口#
要将旧版脚本从旧版 API 升级到新版 API,必须对旧版脚本进行几处修改。
其中最重要的一点是,您不再需要像在旧 API 中那样调用实体。
Old API
# Old API
>>> mapdl.geometry.areas()
[UnstructuredGrid (0x7f14add95040)
N Cells: 12
N Points: 20
X Bounds: -2.000e+00, 2.000e+00
Y Bounds: 0.000e+00, 1.974e+00
Z Bounds: 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00
N Arrays: 4,
UnstructuredGrid (0x7f14add95ca0)
N Cells: 12
N Points: 20
X Bounds: -2.000e+00, 2.000e+00
Y Bounds: 0.000e+00, 1.974e+00
Z Bounds: 5.500e-01, 5.500e-01
N Arrays: 4,
...
New API
>>> mapdl.geometry.areas
MultiBlock (0x147ca7640)
N Blocks 28
X Bounds -0.016, 0.016
Y Bounds -0.008, 0.018
Z Bounds -0.003, 0.015
此外,这些方法返回的实体类型也不同。本表比较了新旧 API 返回的对象:
Table 2. Comparison between objects returned by both APIs.
Function |
Old API (Function based - Must be called) |
New API (Property based - Doesn’t need to be called) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
Not existent |
该表显示了新旧 API 之间的等效性:
Table 3. Equivalence between both API methods.
Old API |
New API equivalent |
|---|---|
Not existent |
MAPDL geometry commands#
有关创建几何图形的其他 MAPDL 命令,请参阅 Preprocessing 命令。