Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
排气歧管的热结构分析#
本例说明如何映射 CFD 分析结果并执行有限元 (FE) 分析。
Objective#
在本例中,我们将进行有限元分析,计算排气歧管中产生的热应力。歧管由结构钢制成,其中的温度分布通过 CFD 运行获得。 我们导入这些数据并将其映射到 FE 网格上,然后使用高斯插值内核定义每个节点的热负荷。

Procedure#
启动 MAPDL 实例
导入几何体、分配材料属性并生成 FE 网格。
导入温度分布并将其映射到 FE 网格上
定义边界条件并使用导入的温度分布来定义热负荷。
求解模型并绘制相关结果。
Additional Packages used#
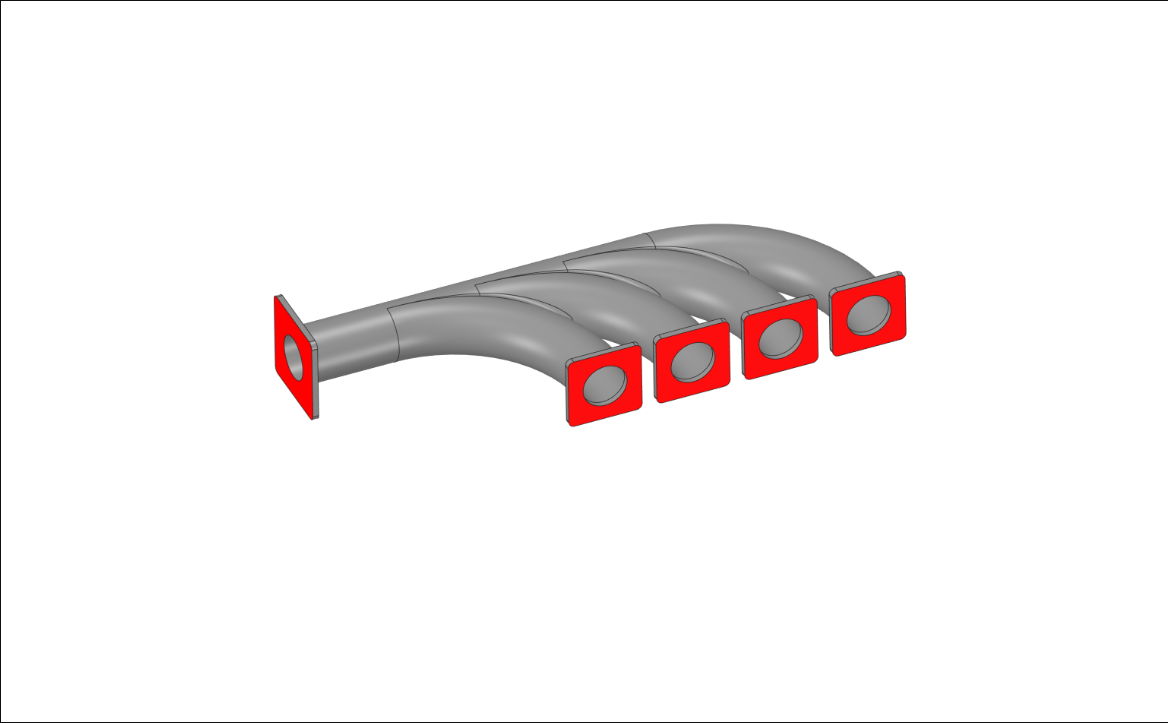
Boundary Conditions#
Highlighted faces are fully constrained.
Import all necessary modules and launch an instance of MAPDL#
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import pyvista as pv
from ansys.mapdl.core import launch_mapdl
from ansys.mapdl.core.examples import download_manifold_example_data
# start mapdl
mapdl = launch_mapdl()
print(mapdl)
Product: Ansys Mechanical Enterprise
MAPDL Version: 23.1
ansys.mapdl Version: 0.67.0
Import geometry, assign material properties and generate a mesh.#
# download the necessary files
paths = download_manifold_example_data()
geometry = paths["geometry"]
mapping_data = paths["mapping_data"]
# reset mapdl & import geometry
mapdl.clear()
mapdl.input(geometry)
# Define element attributes
# Second-order tetrahedral elements (SOLID187)
mapdl.prep7()
mapdl.et(1, "SOLID187")
# Define material properties of structural steel
E = 2e11 # Youngs modulus
NU = 0.3 # Poisson's ratio
CTE = 1.2e-5 # Coeff. of thermal expansion
mapdl.mp("EX", 1, E)
mapdl.mp("PRXY", 1, NU)
mapdl.mp("ALPX", 1, CTE)
# Define mesh controls and generate mesh
mapdl.esize(0.0075)
mapdl.vmesh("all")
# Save mesh as VTK object
print(mapdl.mesh)
grid = mapdl.mesh.grid # save mesh as a VTK object
ANSYS Mesh
Number of Nodes: 87614
Number of Elements: 44266
Number of Element Types: 1
Number of Node Components: 0
Number of Element Components: 0
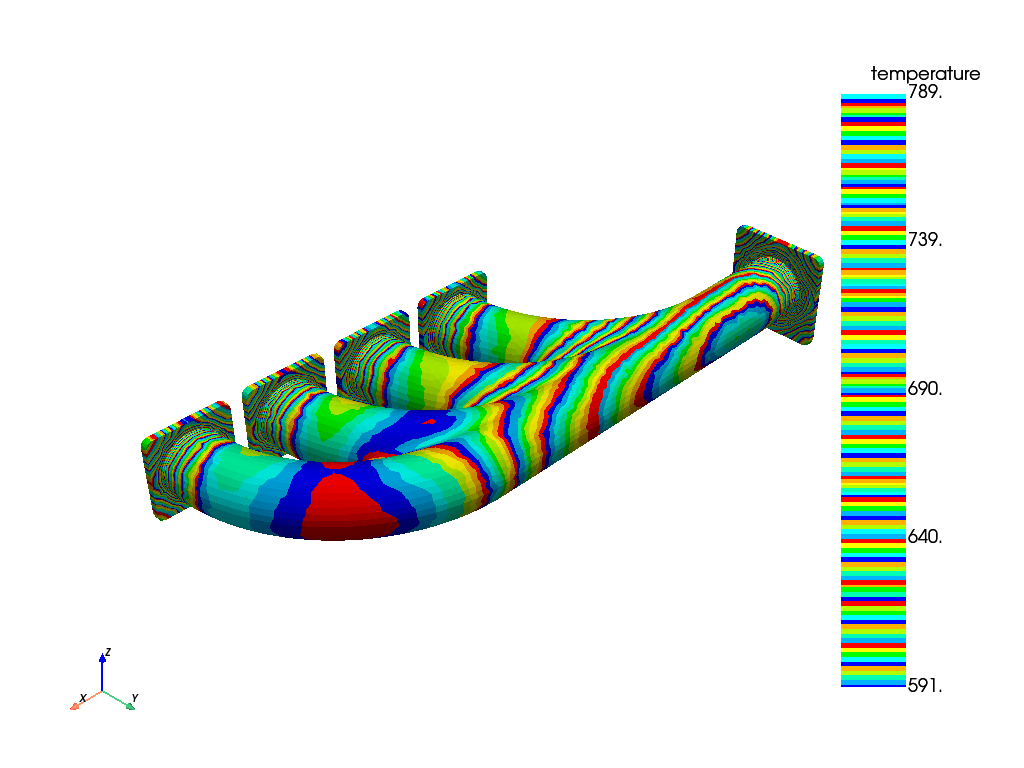
Import and map temperature data to FE mesh#
# Import csv file and save data to a NumPy array
temperature_file = pd.read_csv(mapping_data, sep=",", header=None, low_memory=False)
temperature_data = temperature_file.values # Save data to a NumPy array
nd_temp_data = temperature_data[1:, 1:].astype(float) # Change data type to Float
# Map temperature data to FE mesh
# Convert imported data into PolyData format
wrapped = pv.PolyData(nd_temp_data[:, :3]) # Convert NumPy array to PolyData format
wrapped["temperature"] = nd_temp_data[
:, 3
] # Add a scalar variable 'temperature' to PolyData
# Perform data mapping
inter_grid = grid.interpolate(
wrapped,
sharpness=5,
radius=0.0001,
strategy="closest_point",
progress_bar=True,
) # Map the imported data to MAPDL grid
inter_grid.plot(show_edges=False) # Plot the interpolated data on MAPDL grid
temperature_load_val = pv.convert_array(
pv.convert_array(inter_grid.active_scalars)
) # Save temperatures interpolated to each node as NumPy array
node_num = inter_grid.point_data["ansys_node_num"] # Save node numbers as NumPy array
0%| [00:00<?]
Interpolating: 0%| [00:00<?]
Interpolating: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████[00:00<00:00]
Interpolating: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████[00:00<00:00]
Apply loads and boundary conditions and solve the model#
# Read all nodal coords. to an array & extract the X and Y min. bounds
array_nodes = mapdl.mesh.nodes
Xmin = np.amin(array_nodes[:, 0])
Ymin = np.amin(array_nodes[:, 1])
# Enter /SOLU processor to apply loads and BCs
mapdl.finish()
mapdl.slashsolu()
# Enter non-interactive mode to assign thermal load at each node using imported data
with mapdl.non_interactive:
for node, temp in zip(node_num, temperature_load_val):
mapdl.bf(node, "TEMP", temp)
# Use the X and Y min. bounds to select nodes from five surfaces that are to be fixed and created a component and fix all DOFs.
mapdl.nsel("s", "LOC", "X", Xmin) # Select all nodes whose X coord.=Xmin
mapdl.nsel(
"a", "LOC", "Y", Ymin
) # Select all nodes whose Y coord.=Ymin and add to previous selection
mapdl.cm("fixed_nodes", "NODE") # Create a nodal component 'fixed_nodes'
mapdl.allsel() # Revert active selection to full model
mapdl.d(
"fixed_nodes", "all", 0
) # Impose fully fixed constraint on component created earlier
# Solve the model
output = mapdl.solve()
print(output)
*** NOTE *** CP = 23.875 TIME= 00:31:54
The automatic domain decomposition logic has selected the MESH domain
decomposition method with 2 processes per solution.
***** MAPDL SOLVE COMMAND *****
*** WARNING *** CP = 23.922 TIME= 00:31:54
Previous testing revealed that 123 of the 44266 selected elements
violate shape warning limits. To review warning messages, please see
the output or error file, or issue the CHECK command.
*** NOTE *** CP = 23.922 TIME= 00:31:54
The model data was checked and warning messages were found.
Please review output or errors file (
C:\Users\ff\AppData\Local\Temp\ansys_fdcyykaruq\file0.err ) for these
warning messages.
*** SELECTION OF ELEMENT TECHNOLOGIES FOR APPLICABLE ELEMENTS ***
---GIVE SUGGESTIONS ONLY---
ELEMENT TYPE 1 IS SOLID187. IT IS NOT ASSOCIATED WITH FULLY INCOMPRESSIBLE
HYPERELASTIC MATERIALS. NO SUGGESTION IS AVAILABLE.
*** MAPDL - ENGINEERING ANALYSIS SYSTEM RELEASE 2023 R1 23.1 ***
Ansys Mechanical Enterprise
20120530 VERSION=WINDOWS x64 00:31:54 JAN 24, 2024 CP= 23.938
File: D:\AICs\PyAnsys\Getting Started With PyMAPDL\Dataflow Between Python an
S O L U T I O N O P T I O N S
PROBLEM DIMENSIONALITY. . . . . . . . . . . . .3-D
DEGREES OF FREEDOM. . . . . . UX UY UZ
ANALYSIS TYPE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .STATIC (STEADY-STATE)
GLOBALLY ASSEMBLED MATRIX . . . . . . . . . . .SYMMETRIC
*** NOTE *** CP = 23.969 TIME= 00:31:54
Present time 0 is less than or equal to the previous time. Time will
default to 1.
*** NOTE *** CP = 23.969 TIME= 00:31:54
The conditions for direct assembly have been met. No .emat or .erot
files will be produced.
D I S T R I B U T E D D O M A I N D E C O M P O S E R
...Number of elements: 44266
...Number of nodes: 87614
...Decompose to 2 CPU domains
...Element load balance ratio = 1.000
L O A D S T E P O P T I O N S
LOAD STEP NUMBER. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
TIME AT END OF THE LOAD STEP. . . . . . . . . . 1.0000
NUMBER OF SUBSTEPS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
STEP CHANGE BOUNDARY CONDITIONS . . . . . . . . NO
PRINT OUTPUT CONTROLS . . . . . . . . . . . . .NO PRINTOUT
DATABASE OUTPUT CONTROLS. . . . . . . . . . . .ALL DATA WRITTEN
FOR THE LAST SUBSTEP
SOLUTION MONITORING INFO IS WRITTEN TO FILE= file.mntr
Range of element maximum matrix coefficients in global coordinates
Maximum = 1.590000175E+11 at element 2593.
Minimum = 317042229 at element 29914.
*** ELEMENT MATRIX FORMULATION TIMES
TYPE NUMBER ENAME TOTAL CP AVE CP
1 44266 SOLID187 1.391 0.000031
Time at end of element matrix formulation CP = 24.984375.
DISTRIBUTED SPARSE MATRIX DIRECT SOLVER.
Number of equations = 251964, Maximum wavefront = 270
Process memory allocated for solver = 581.364 MB
Process memory required for in-core solution = 557.506 MB
Process memory required for out-of-core solution = 218.250 MB
Total memory allocated for solver = 1169.853 MB
Total memory required for in-core solution = 1121.657 MB
Total memory required for out-of-core solution = 438.542 MB
*** NOTE *** CP = 25.500 TIME= 00:31:56
The Distributed Sparse Matrix Solver is currently running in the
in-core memory mode. This memory mode uses the most amount of memory
in order to avoid using the hard drive as much as possible, which most
often results in the fastest solution time. This mode is recommended
if enough physical memory is present to accommodate all of the solver
data.
Distributed sparse solver maximum pivot= 2.447219091E+11 at node 53378
UY.
Distributed sparse solver minimum pivot= 100225135 at node 42731 UZ.
Distributed sparse solver minimum pivot in absolute value= 100225135 at
node 42731 UZ.
*** ELEMENT RESULT CALCULATION TIMES
TYPE NUMBER ENAME TOTAL CP AVE CP
1 44266 SOLID187 1.422 0.000032
*** NODAL LOAD CALCULATION TIMES
TYPE NUMBER ENAME TOTAL CP AVE CP
1 44266 SOLID187 0.250 0.000006
*** LOAD STEP 1 SUBSTEP 1 COMPLETED. CUM ITER = 1
*** TIME = 1.00000 TIME INC = 1.00000 NEW TRIANG MATRIX
*** MAPDL BINARY FILE STATISTICS
BUFFER SIZE USED= 16384
60.750 MB WRITTEN ON ASSEMBLED MATRIX FILE: file0.full
21.875 MB WRITTEN ON RESULTS FILE: file0.rst
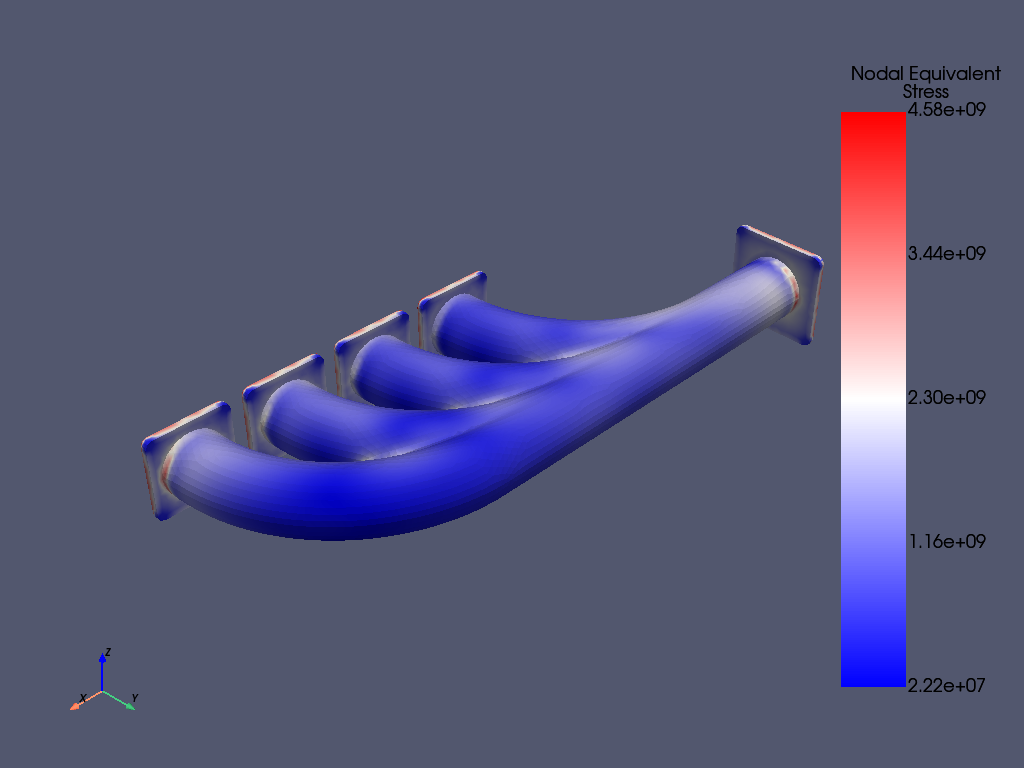
Post-processing#
# Enter post-processor
mapdl.post1()
mapdl.set(1, 1) # Select first load step
mapdl.post_processing.plot_nodal_eqv_stress() # Plot equivalent stress
Exit MAPDL instance#
mapdl.exit()
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 36.470 seconds)